|
|
|
|
| public class NormalGenerator extends ChunkGenerator { private SimplexOctaveGenerator noise; @Override public ChunkData generateChunkData(World world, Random random, int chunkX, int chunkZ, BiomeGrid biome) { ChunkData chunkData = createChunkData(world); // 我们需要的噪声生成器 if (noise == null) { noise = new SimplexOctaveGenerator(world.getSeed(), 1); // 我们需要更平缓的地形,所以需要设置 scale // 该值越大,地形变化更大 // 微调即可 noise.setScale(0.005D); } for (int x = 0; x < 16; x++) { for (int z = 0; z < 16; z++) { // 方块的真实坐标 int realX = chunkX * 16 + x; int realZ = chunkZ * 16 + z; // noise 方法返回 -1 到 1 之间的随机数 double noiseValue = noise.noise(realX, realZ, 0.5D, 0.5D); // 将 noise 值放大,作为该点的高度 int height = (int) (noiseValue * 40D + 100D); // 底层基岩 chunkData.setBlock(x, 0, z, Material.BEDROCK); // 中间石头 for (int y = 0; y < height - 1; y++) { chunkData.setBlock(x, y, z, Material.STONE); } // 表面覆盖泥土和草方块 chunkData.setBlock(x, height - 1, z, Material.DIRT); chunkData.setBlock(x, height, z, Material.GRASS_BLOCK); } } return chunkData; } } |
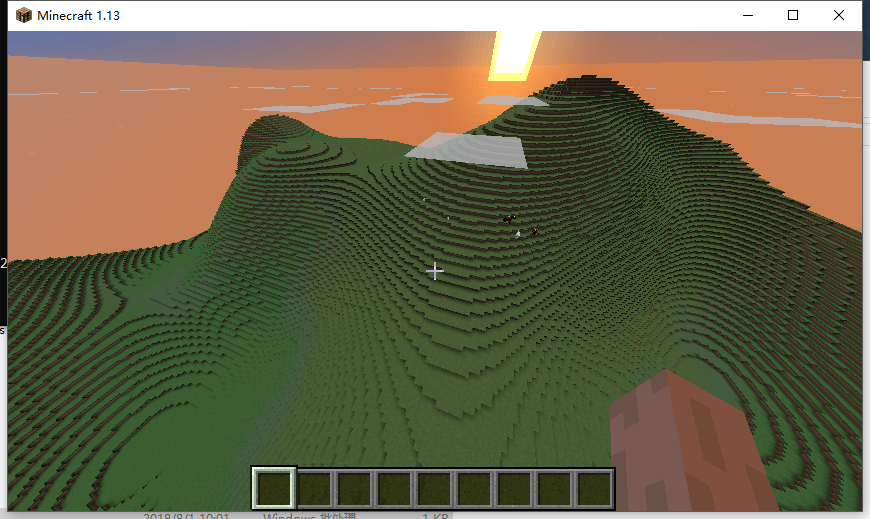
| @Override public List<BlockPopulator> getDefaultPopulators(World world) { return ImmutableList.of(new TreePopulator()); } private static class TreePopulator extends BlockPopulator { @Override public void populate(World world, Random random, Chunk chunk) { // 假设只有 1/4 的区块生成树 if (random.nextInt(4) < 1) { // 假设每个区块生成 1-3 颗树 int amount = random.nextInt(3) + 1; for (int i = 0; i < amount; i++) { // 随机生成树的坐标 int x = random.nextInt(16); int z = random.nextInt(16); int y = 255; // 找到最高的方块来生成树 while (chunk.getBlock(x, y, z).getType() == Material.AIR) y--; // 生成树 world.generateTree(chunk.getBlock(x, y, z).getLocation(), // 搞点有趣的,我们随机选择不同的树生成 TreeType.values()[random.nextInt(TreeType.values().length)]); } } } } |
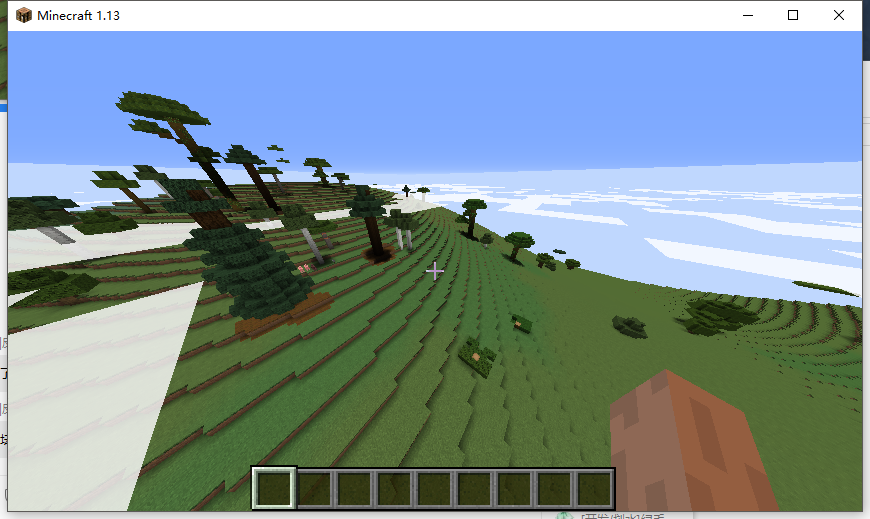
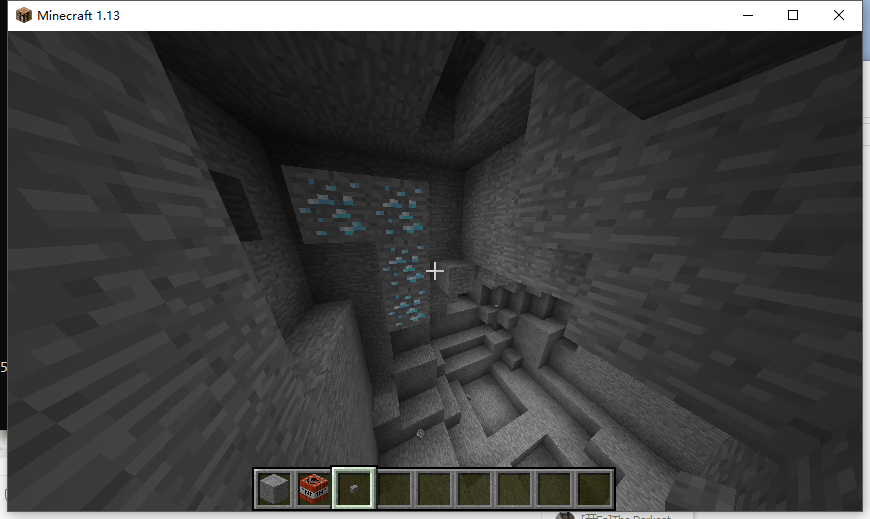
| @Override public List<BlockPopulator> getDefaultPopulators(World world) { return ImmutableList.of(new TreePopulator(), new DiamondPopulator()); } private static class DiamondPopulator extends BlockPopulator { @Override public void populate(World world, Random random, Chunk chunk) { // 假设每个区块只有一个钻石矿 // 钻石矿脉随机生成在高度 16 以下 int x = random.nextInt(16); // 不要生成在基岩上 int y = random.nextInt(15) + 1; int z = random.nextInt(16); // 继续生成的几率 while (random.nextDouble() < 0.8D) { // 只替换岩石 if (chunk.getBlock(x, y, z).getType() == Material.STONE) { chunk.getBlock(x, y, z).setType(Material.DIAMOND_ORE); } // 向某个方向随机继续生成 switch (random.nextInt(6)) { case 0: x++; break; case 1: y++; break; case 2: z++; break; case 3: x--; break; // 不要生成到基岩下面去了 case 4: y = Math.max(y-1, 0); break; default: z--; break; } } } } |
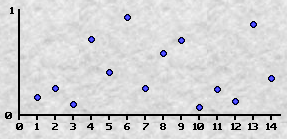
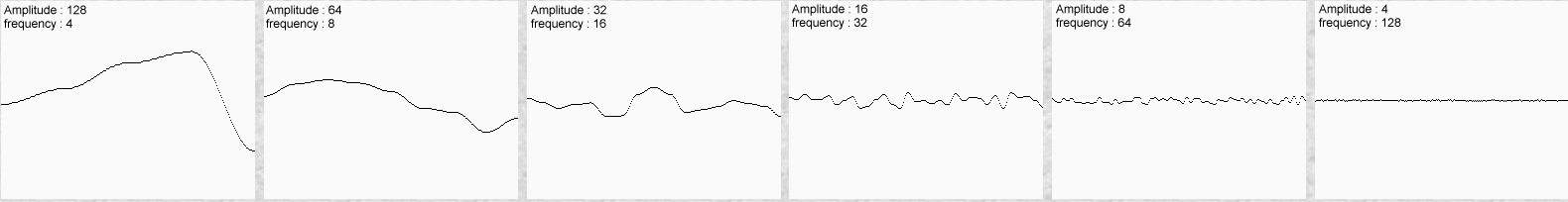
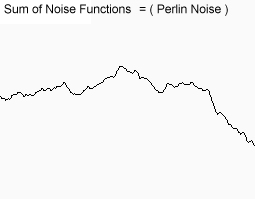
| /** * 假设此函数返回 0-1 之间的随机数,并且满足噪波函数的相关定义 * * @param x 参数 * @return 0-1 的随机数 */ static double noise(double x) { return 0; } /** * 噪波函数 * * @param x 参数 * @param freq 频率 * @param amp 振幅 * @return 函数值 */ static double f(double x, double freq, double amp) { return amp * noise(x * freq); } static double f(double x) { return f(x, 1, 1) + f(x, 2, 0.5) + f(x, 4, 0.25) + f(x, 8, 0.125); } |
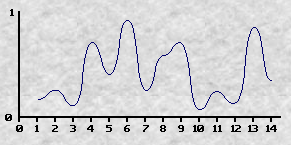
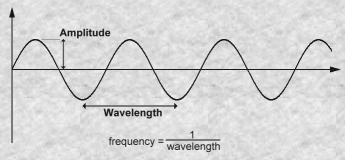
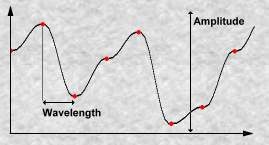
| 维基百科: 分形噪声是上述 Perlin 1985年的文章中提出的将符合上文所述三条件的噪声通过计算分形和构造更复杂效果的算法。 在一维的情况下,设噪声函数为noise(x),则通过 noise(2x), noise(4x) 等就可以构造更高频率的噪声。 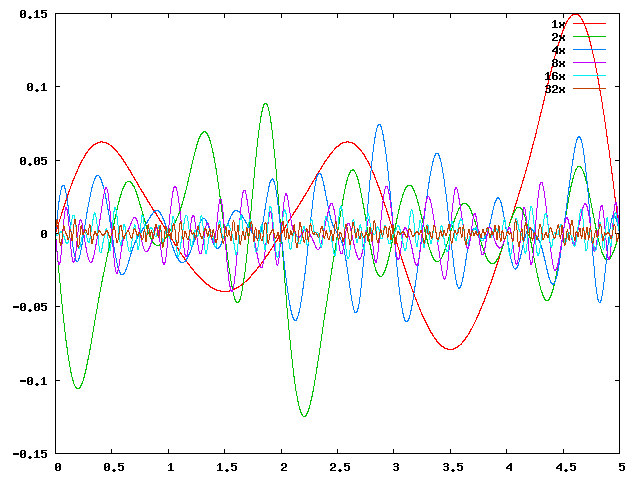  |
| static double f(double x, double freq, double amp, int octaves, boolean normalized) { double result = 0.0D; double a = 1.0D; double f = 1.0D; double max = 0.0D; for (int i = 0; i < octaves; ++i) { result += f(x, f, a); max += amp; f *= freq; a *= amp; } if (normalized) { result /= max; } return result; } |
| static double bukkitNoise(double x, double freq, double amp, int octaves, boolean normalized) { SimplexNoiseGenerator generator = new SimplexNoiseGenerator(new Random()); return generator.noise(x, octaves, freq, amp, normalized); } static double bukkitOctave(double x, double freq, double amp, int octaves, boolean normalized) { SimplexOctaveGenerator generator = new SimplexOctaveGenerator(new Random(), octaves); return generator.noise(x, freq, amp, normalized); } |
| n1 = new PerlinNoiseGenerator(random); double e = n1.noise(x * 0.01F, z * 0.01F, 6, 2.0F, 0.5F); e = Math.pow(e, 2.5); elevation[x][z] = (int) (64 + e * 64F); |
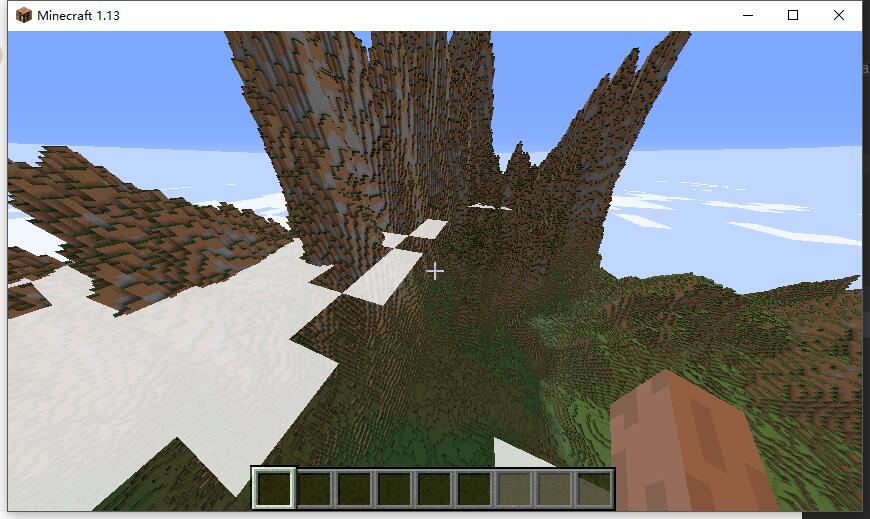
| function ridgenoise(x, z) { return 2 * (0.5 - abs(0.5 - noise(x, z))); } e0 = 1 * ridgenoise(1 * x, 1 * z); e1 = 0.5 * ridgenoise(2 * x, 2 * z) * e0; e2 = 0.25 * ridgenoise(4 * x, 4 * z) * (e0+e1); e = e0 + e1 + e2; elevation[x][z] = Math.pow(e, 2.5); |
 感谢感谢
感谢感谢 